[ad_1]
Decentralized finance, or DeFi, has revolutionized business and unlocked new value across every industry sector. However, significant problems have emerged with blockchain technology, hindering the unlocking of the full potential of Web 3. Vitalik Buterin, the Ethereum blockchain co-founder, has postulated a so-called “blockchain trilemma,” meaning a blockchain is unable to deliver decentralization, scalability, and security at the same time, so developers have to make trade-offs between them.
The DeFi boom is exposing Ethereum’s scalability issues and ability to cope with increased usage leading to network congestion and higher gas fees for processing transactions on the Network. Ethereum’s response to these issues is the long-awaited Ethereum 2.0 (since 2014), which would make Ethereum simultaneously more scalable, secure, and sustainable while still remaining decentralized.
Meanwhile, Solana is another highly functional open-source web-scale blockchain with a permissionless nature offering an ambitious design that aims to solve the blockchain trilemma. Matt Hougan, chief investment officer at Bitwise Asset Management, calls Solana a “leading Ethereum competitor.”
So how do Solana and Ethereum differ? This review will present a Solana vs. Ethereum detailed comparison and dive deep into the key features, ecosystems, advantages, and drawbacks of the Ethereum Network and Solana.
Let’s get started!
Ethereum Pros
- The world’s most prominent DApp and DeFi ecosystem
- Allows the development and deployment of smart contracts
- Zero downtime
- Secure, decentralized, and efficient.
Ethereum Cons
- Requires substantial processing power
- Slow transaction speed
- High gas fees.
Solana Pros
- Low transaction fees
- No congestion, processing 50,000 transactions per second (TPS)
- Scalable protocol.
Solana Cons
- Lack of decentralization
- Protocol experiences sporadic halts.
Ethereum or Solana: Initial Facts
Ethereum and Solana both provide smart contracts that are crucial in running DApps and NFTs but with different transaction speeds. It’s essential to understand what unites Ethereum and Solana, as well as the unique features of each blockchain, before investing.
Ethereum Network
In 2013 Ethereum Network was created as the first competitor to Bitcoin by a group of developers, including Vitalik Buterin, Gavin Wood (Polkadot founder), and Charles Hoskinson (head of Cardano).
Ethereum changed the blockchain industry forever by becoming the first smart contract programmable blockchain.
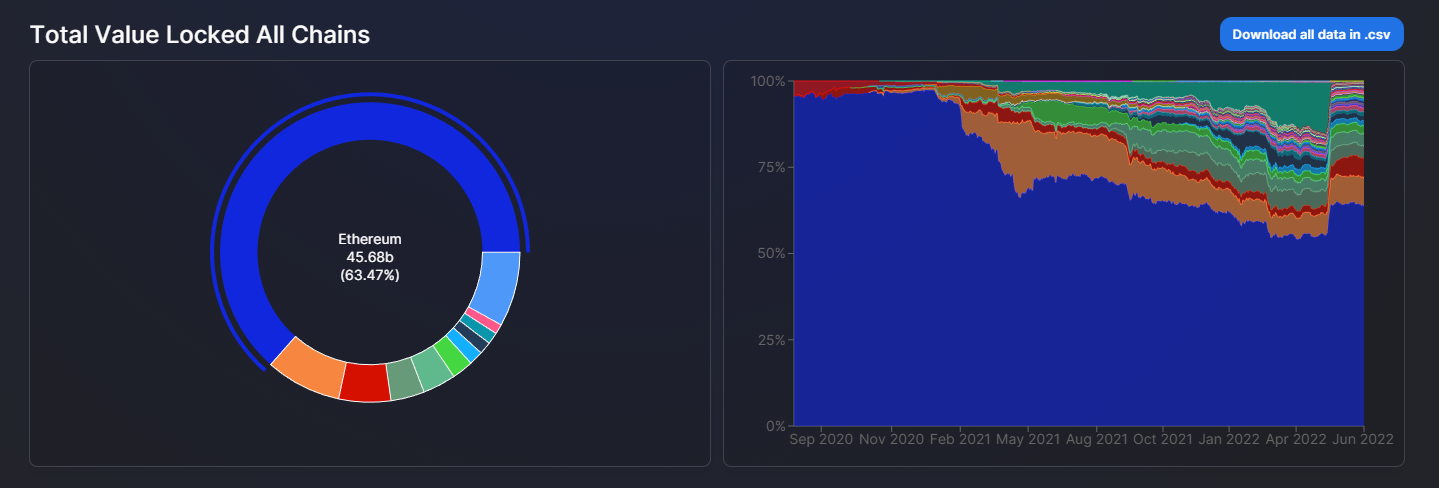
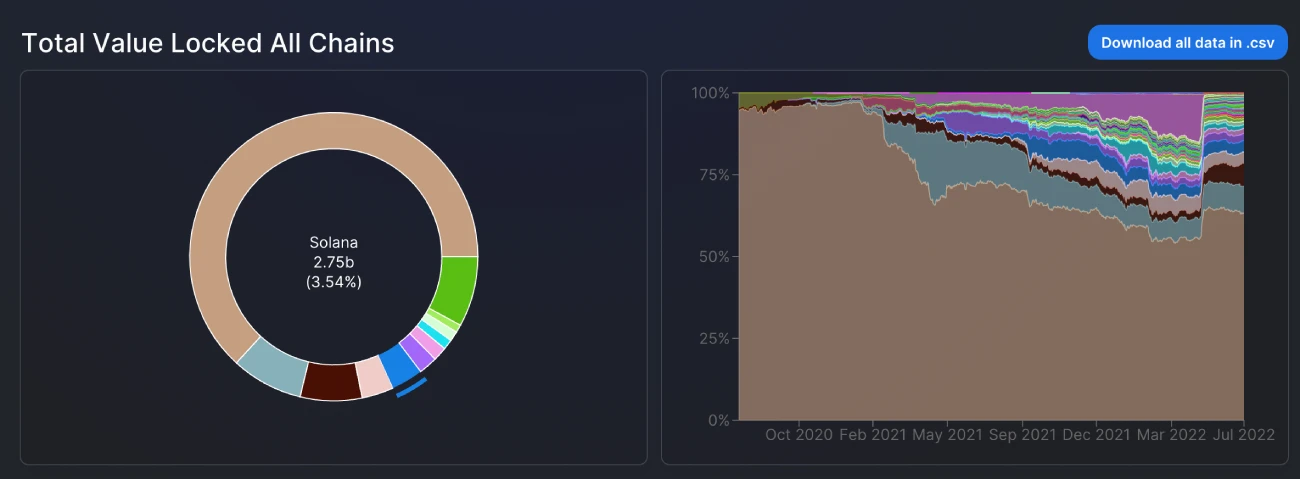
Ethereum’s token Ether (ETH) is currently the second-largest crypto in the market according to DeFi Llama. Meanwhile, Ethereum, a blockchain that offers a transparent and advanced DApps ecosystem, dominates the DeFi market by a large margin, with a market cap of $49.1 billion, while Solana comes fifth with a market cap of $2.75 billion.
As the frenzy around various decentralized applications (DApps) and non-fungible tokens (NFTs) intensifies, the competition between layer one protocols grows fiercer.
Ethereum is the first blockchain to offer smart contract functionality and the most prominent blockchain for Layer 2 project development; however, its Proof of Work (PoW) mining system and high gas fees have proven to impede transaction speed and scalability within its DeFi ecosystem.
In 2021, several smart contract-enabled Layer 1 blockchains were created to address these issues by promising higher transaction speeds at lower costs — something Ethereum lacks and aims to achieve using its Ethereum 2.0 upgrade. Solana is one such highly functional open-source project that implements a new, permissionless, and high-speed layer-1 blockchain aiming to deliver high throughput and low costs.
Solana Network
Anatoly Yakovlenko founded Solana in 2017. The Solana network implements an innovative hybrid consensus model as an attempt to solve the blockchain trilemma. It combines a unique Proof-of-History (PoH) algorithm with a lightning-fast synchronization engine, a version of Proof-of-Stake (PoS) to process over 710,000 transactions per second (TPS).
Solana facilitates smart contracts and DApp creation and supports a wide range of DeFi platforms and NFT marketplaces.
Solana’s native toke SOL provides a means of transferring value and blockchain security through staking. SOL was launched in March 2020 to become one of the top 10 cryptocurrencies in the crypto market by total market capitalization.
Let’s address the core differences between Solana and Ethereum below.
The key difference in the Solana vs. Ethereum comparison lies in the consensus mechanism, a mandatory procedure followed by all blockchain nodes to reach agreements regarding the present state of the Network.
Ethereum’s Proof-of-Work Consensus Mechanism
Ethereum presently leverages the PoW consensus mechanism, drawing power from multiple miners worldwide participating actively in the consensus. PoW consensus demands high computing power, thereby restricting the scope of participation for users. It helps ensure security and complete decentralization for ETH, but it also suffers from concerns of reduced performance.
By the end of September 2022, the entire Network will transit to an alternative consensus mechanism – Proof-of-Stake (PoS). Ethereum is set to replace the PoW, the environmentally unfriendly consensus mechanism it uses today, with the much more eco-friendly PoS mechanism. PoS dramatically reduces energy consumption by making mining obsolete. Instead, PoS relies on a system of validators, or nodes, to verify each transaction.
Solana’s Proof-of-History Consensus Mechanism
The Solana Network uses a unique hybrid consensus mechanism that features the best of Proof-of-Stake and Proof-of-History. The hybrid consensus on the Solana blockchain enables better flexibility for arranging the order of transactions enabling around 50,000 transactions per second.
The PoH is a system that enables transaction verification through time stamps. The PoH computational sequence creates a historical record proving that an event has occurred at a specific moment in time. It incorporates a system for timestamping transactions to evaluate and eventually produce a unique output that can be verified publicly. As a result, validators all have a “uniform view of the order” in which new transactions appear on the blockchain. Network participants analyze the validity of transactions and must agree on a single history of events – this is why the system is called the Proof-of-History (PoH) consensus.
The innovative combination of PoS and PoH makes Solana a unique project in the blockchain industry.
Another essential criterion for Solana vs. Ethereum comparison is the blockchain architecture.
Ethereum Network provides the true example of stateful architecture by recording all the transactions on the Network in the existing state. When a new transaction happens, the entire Network must update its copies of the transaction to reflect the recent transaction. Naturally, the constant update takes time and energy and is partially responsible for the congestion plaguing Ethereum.
On the other hand, Solana has a stateless architecture, with no need to update the whole state of the Solana blockchain with every new transaction. Solana’s architecture relies heavily on the Solana cluster, a collection of validators working together to address client transactions alongside ledger maintenance. Every cluster has its own leader, and the role continues rotating among the validators. The cluster leader is responsible for bundling and timestamping the incoming transactions using PoH consensus. Its stateless architecture provides fast and low-cost transactions.
Solana also uses the Tower Byzantine fault tolerance (BFT) algorithm, an improvised version of pBFT (practical Byzantine fault tolerance ) that removes the need for nodes to communicate with each other in real-time, thereby improving the overall efficiency.
Smart contracts functionality is what initiated the entire DeFi industry. In short, smart contracts are computer programs, or transaction protocols, which intend to automatically execute or document a legal event (such as a money transaction) according to the terms of the contract.
Ethereum Network was the first to introduce smart contract functionality to the blockchain technology, while the rest of the Layer 1 platforms, including Solana, implemented the system on their blockchains.
The Solana network, however, offers a smart contract functionality that differs from other projects, in which smart contracts may interfere with one another since they can’t operate in parallel.
Solana uses Sealevel, a system that allows smart contracts to run side by side without causing any disruptions. This gives Solana a significant advantage in terms of performance levels in the Network.
Scalability
The core difference between Solana and Ethereum refers to scalability. Scalability is the property of a system to handle a growing amount of work by adjusting its efficiency or adding resources.
Regarding Ethereum, scalability is the number one issue the Network has to deal with. Despite the high gas fees, the number of DApps on the blockchain multiplies, requiring more and more validation and a higher transaction speed.
The transaction speed on Ethereum is only 15 transactions per second, so the scalability problem can only be resolved through the development of Layer 2 scaling solutions and support for multi-chain networks, from state channels to sidechains, i.e., Validium and Rollups (Optimistic). Ethereum also supports multi-chain networks, such as Polygon, that help enhance its scalability without compromising security.
On the other hand, Solana addresses the scalability issue with a high-performance protocol that offers innovative time architecture, improved transaction processing speeds, and an efficient consensus model. This means that Solana doesn’t require Layer 2 solutions to enhance scalability. Moreover, Solana achieves scalability by employing the Turbine block propagation protocol that breaks down data into smaller fragments to transfer it across the Network easily.
Ecosystem
The Ethereum and Solana ecosystems are incomparable in size.
Ethereum features a diverse family of DApps, from decentralized exchanges to NFT marketplaces, stablecoins, lending, and gaming protocols.
Some of the most successful protocols running on Ethereum include Tether stablecoin, SushiSwap decentralized exchange, Opensea, the largest NFT marketplace, etc. Moreover, Ethereum supports a rich suite of tokens.
Here’s a list of the top 10 tokens by market cap running on the Ethereum Network.
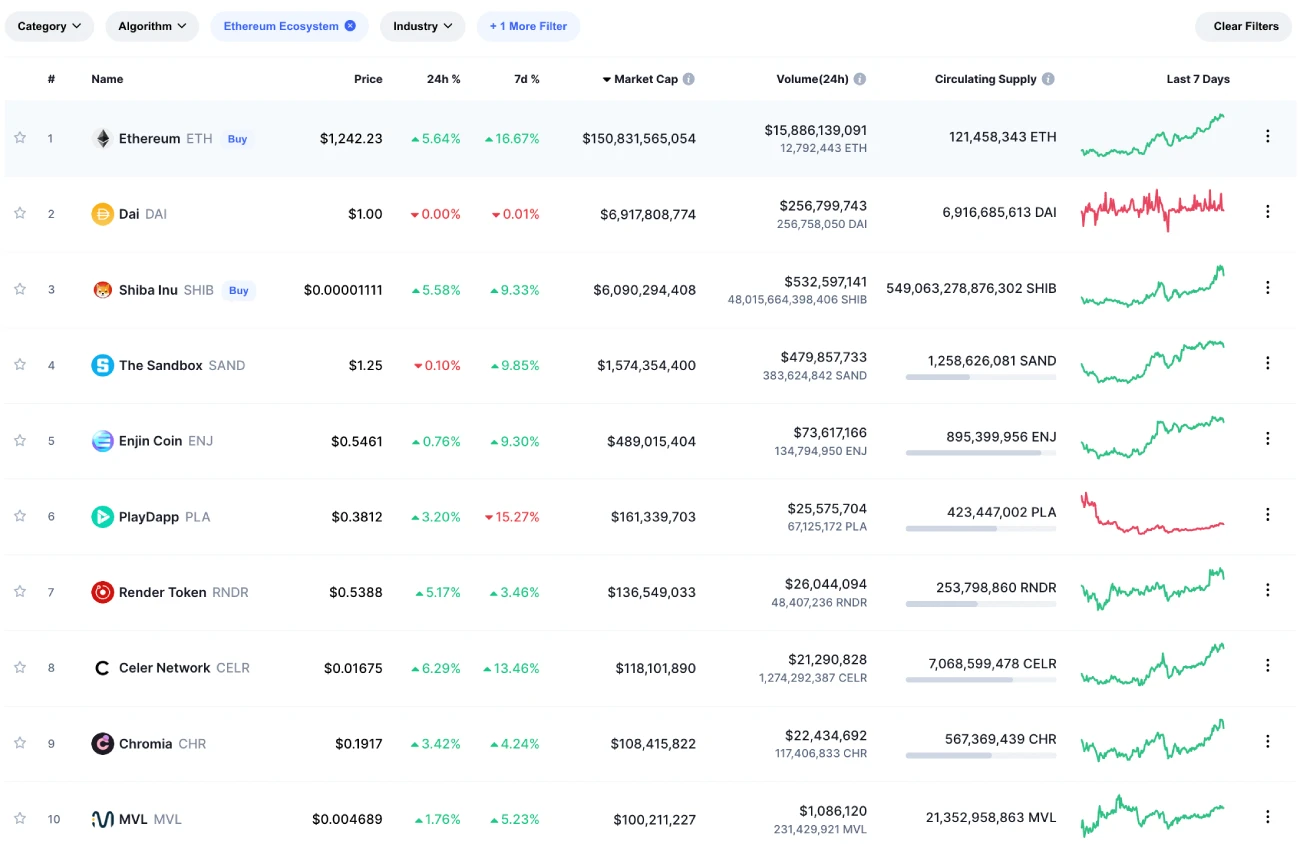
The list includes several leading tokens, such as USD Coin stablecoin, Shiba Inu meme coin, and Polygon.
While Solana is a young platform compared to Ethereum, it still features a considerable amount of tokens, decentralized exchanges, lending/borrowing protocols, NFT marketplaces, etc.
Here is a comprehensive list of the top 10 tokens running on the Solana blockchain:
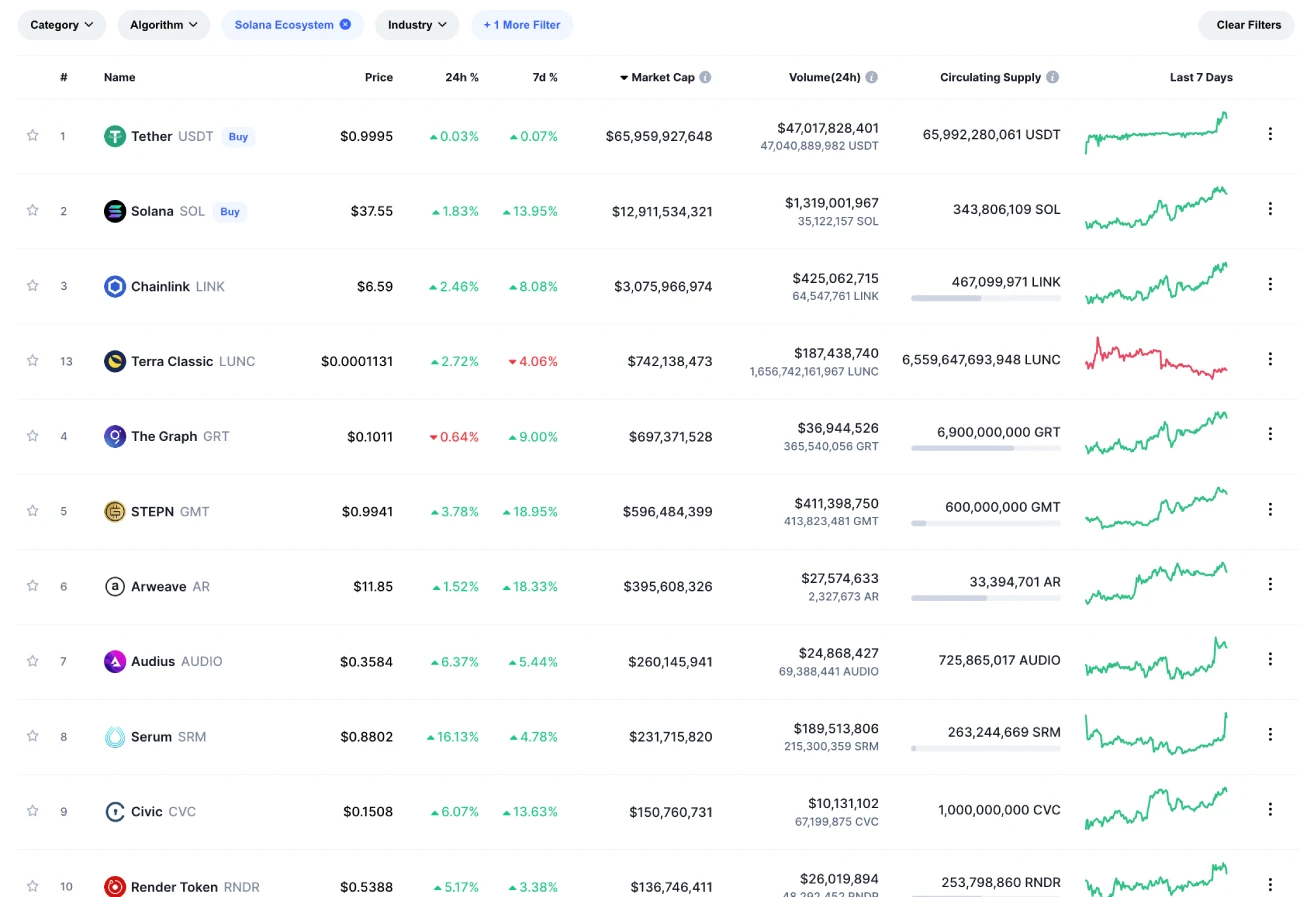
The list includes the leading cryptocurrency Chainlink (LINK) and the move-to-earn platform STEPN’s token GMT.
NFT Trading
NFTs or non-fungible tokens have become an essential part of the DeFi industry.
The largest NFT-trading platform, Opensea, initially started off on Ethereum; however, the marketplace recently announced a partnership with Solana as well. As a result, Solana’s NFT trade boomed, competing in volumes with Ethereum.
Additionally, Solana’s native marketplace Magic Eden significantly contributed to the success. According to DappRadar, Magic Eden has witnessed considerable growth since early April.
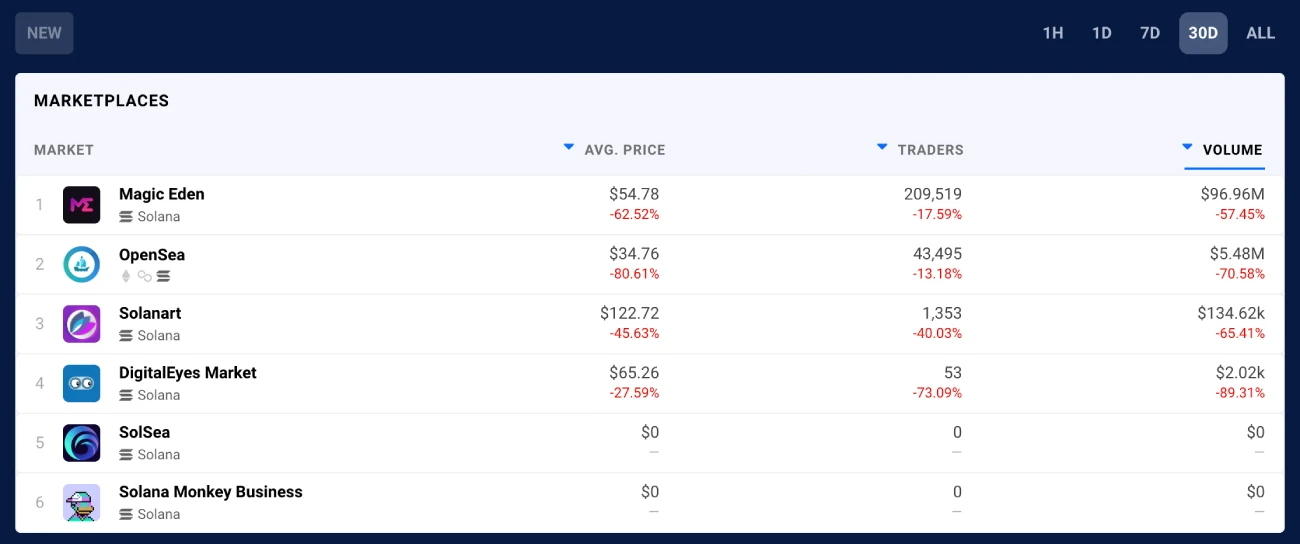
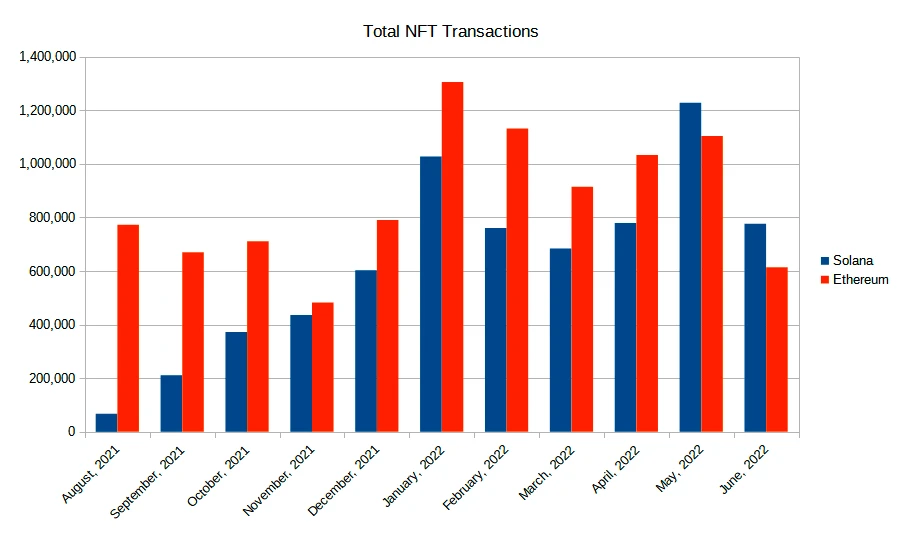
As a result, Solana’s monthly NFT transactions have surpassed Ethereum’s over the last few months.
What Makes Ethereum Network Unique
As mentioned earlier, Ethereum was the foundation for the entire DeFi industry, including the booming NFT market. With a significant first-mover advantage, it is no surprise that Ethereum Networks is currently the largest platform in the crypto market.
As of June 2022, Ethereum hosts nearly 3,000 decentralized applications (DApps) on the blockchain, with more being created monthly. Ethereum’s popularity could be explained by its top-notch security, reliability, and reputation. However, the congestion and high gas fees are among the drawbacks of the Ethereum Network.
Ethereum constantly searches for solutions to achieve faster transaction speeds and enhanced scalability and has introduced several Layer 2 protocols to help with the issues.
What Makes Solana Unique
Solana has positioned itself as a solution to all Ethereum problems, such as scalability, high gas fees, and low transaction speed.
Solana can reach a speed of over 50,000 TPS, and Solana’s unique consensus algorithm makes it one of the fastest blockchains in the industry. Another advantage is Solana’s extreme cost-effectiveness, as the project implements new tokenomics for lower fees. Solana’s blockchain is also more eco-friendly and sustainable than Ethereum.
However, the Solana ecosystem is no match for Ethereum in terms of DApp security and decentralization.

To sum up, Solana is of particular interest to developers and users who are fed up with the high gas fees and slow development pace of the Ethereum network.
Solana vs. Ethereum: Final Verdict
We have extensively discussed both platforms regarding transaction speed, gas fees, scalability, ecosystem, consensus mechanisms, etc. Let’s sum the results up:
- Ethereum has a larger and more reliable ecosystem, while the Solana ecosystem is considerably smaller in size.
- Solana is highly scalable and offers one of the fastest and most efficient ecosystems, while the Ethereum Network is plagued with congestion.
- Solana uses an innovative Proof-of-History system powered by unique algorithms. Ethereum employs the PoW consensus mechanisms to verify transactions.
- Solana offers low-cost transactions, while Ethereum features notoriously high gas fees.
- Solana uses a fraction of the energy resources needed to power the Ethereum virtual machine. Ethereum has yet to transition to the greener Ethereum 2.0.
- Ethereum has experienced hacks in the past but is considered more secure than Solana.
- Ethereum 2.0 was promised for years and is finally scheduled for September 2022. However, Solana developers move considerably faster.
- Ethereum boasts higher decentralization than Solana. Both networks have had unpleasant incidents in the past, but overall, thanks to the still valid PoW consensus, Ethereum wins the decentralization race.
Conclusion
If you’re still wondering which of the two projects is a better investment and whether you should invest, the answer is still up to you. We hope the research into the advantages and demerits of each blockchain project will help you make an informed investment decision.
So, whether you choose Ethereum or Solana will depend on your needs and priorities. Ethereum is more reputable and secure but slower, energy-consuming, and more expensive. Solana is significantly faster, low-cost, and sustainable but smaller and more centralized. Prioritize wisely and remember that this guide is not financial advice. Each trader should do their own research before investing in the volatile crypto market.
Frequently Asked Questions
Ethereum and Solana share similarities; however, they differ in terms of ecosystem size, transaction speed, transaction fees, decentralization, consensus mechanism, etc.
Ethereum offers a more mature DeFi infrastructure powered by a large number of developers. Solana, on the other hand, is a much younger platform, but it provides faster and cheaper transactions without congestion problems. Which is better depends on your specific needs and expectations.
As of June 2022, Solana can process over 50,000 transactions per second (TPS), while Ethereum’s TPS stands at approximately 13. Ethereum is progressing to Ethereum 2.0, and once the upgrade is complete, it will process over 100,000 TPS.
Ethereum takes up over 60% of the DeFi market, while Solana’s share is merely 3.6%. However, Solana is a recent project in constant development and has a dedicated community thanks to its high transaction speed.
[ad_2]
Source link

![Solana vs Еthereum [The Ultimate Guide 2022] Solana vs Еthereum [The Ultimate Guide 2022]](https://coinstats.app/blog/wp-content/uploads/2022/03/CoinStats_blog_og_opt-1.png)